What is Radon Gas?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that comes from the breakdown of uranium in soil, rocks and water. Radon has no order or color and occurs naturally all across the U.S at varying concentrations. Radon gas is one stage of a radioactive decay chain that starts with uranium that then decays into other radioactive elements. Because radon is a gas, it moves easily up through soil and enter homes, schools or businesses. Radon can also be carried by groundwater and natural gas.
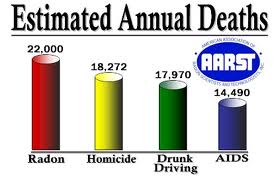
Why is Radon Dangerous?
Radon gas causes lung cancer. The EPA estimates that 21,000 Americans die each year from radon-induced lung cancer. This makes it the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer following smoking. As radon decays, it creates four new elements – collectively known as Radon Decays Products (RDPs) – two of which emit alpha radiation. As these RDPs float around in the air they attach themselves to dust, smoke or other particles which we then breathe in. These particles attach themselves to our sensitive lung tissue and the alpha radiation from the RDPs damages the tissue.
Testing for Radon
The EPA, the Surgeon General, The American Lung Association, and a host of other organizations all strongly recommend that all home buyers test for radon gas. Elevated levels have been found in every state and the potential exists in every community. Accurate testing is the only way to know if you and your family are at risk.The EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter) or more. Because there is no known safe level of exposure to radon, EPA also recommends that Americans consider fixing their home or building for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L.
Radon Mitigation
Radon gas reduction techniques are used to stop radon entry and reduce indoor radon concentrations. There are different methods used, depending on the property configuration.
The most effective measures for reducing radon, without costly renovations, are ones that limit soil gas entry into the building. In general, dangerous vapors are extracted from the soil and rock below the structure then exhausted, safely away from the building, prohibiting radon gas build-up.
One common and very reliable method uses Active Sub-slab Depressurization (SSD). This method uses a radon mitigation exhaust system to reduce the pressure below the floor slab, so that the air between the building substructure and the soil flows out of rather than into the building. Sub-Slab Depressurizations systems are customized for each property, to address specific mitigation requirements. If you have a problem with Radon – give Trinity Radon a call today: 630-499-1492.

Thank you to MWAARST for the great post.




